Architecture
This guide introduces Beamstack’s ecosystem and explains how it fits in the beam pipeline job lifecycle. Read the introduction guide to learn more about Beamstack.
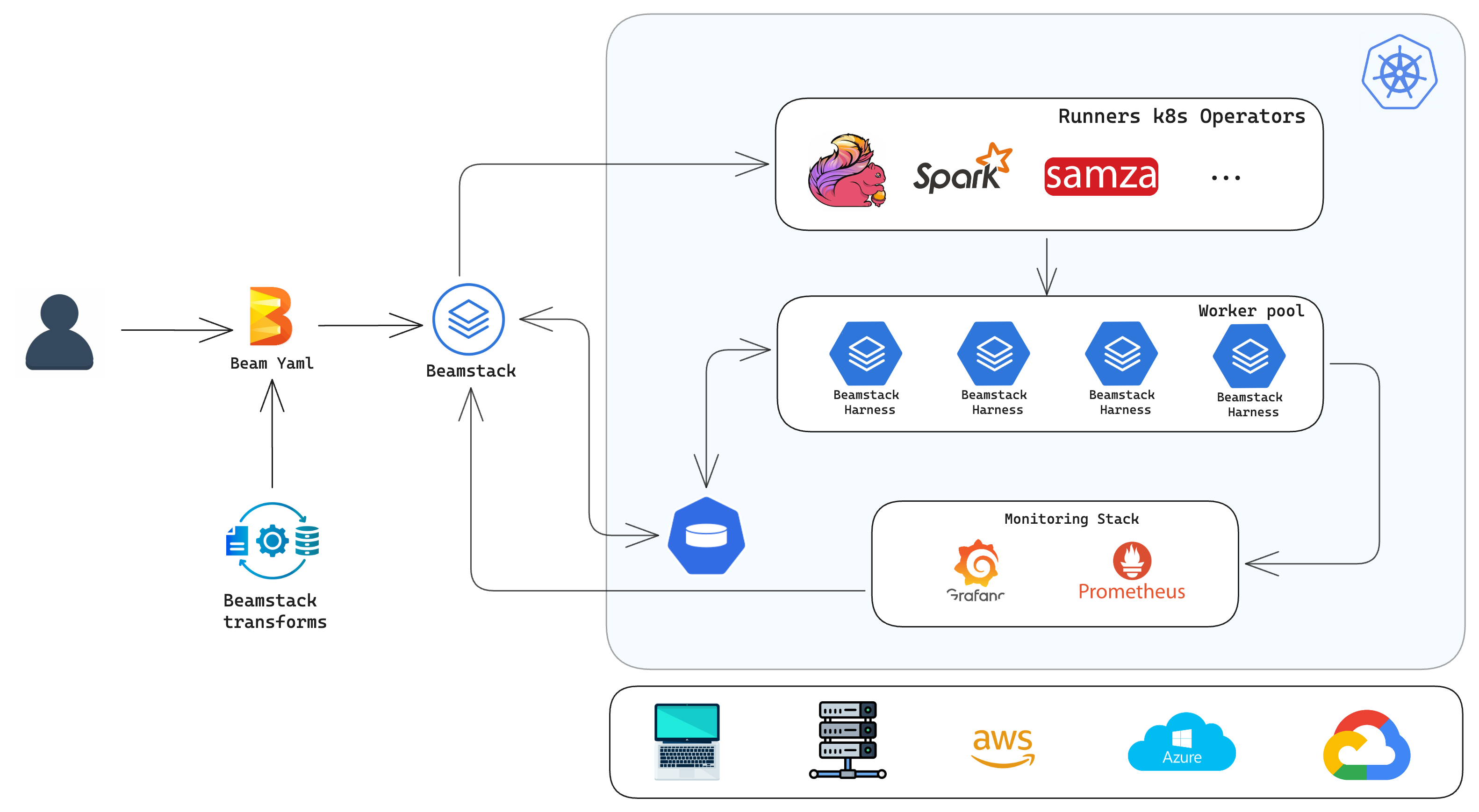
Beamstack Ecosystem
The following diagram gives an overview of the Beamstack Ecosystem and how it relates to the wider Kubernetes and AI/ML landscapes.
Core Components
Beamstack architecture consists of three main components:
Beam Runners Kubernetes Operators:
- Flink, Spark, Samza, etc.
Worker Pool:
- Beamstack Harness for running the pipeline jobs
Monitoring Stack:
- Grafana, Prometheus for monitoring and visualizations
Beam Runners Kubernetes Operators
Beamstack supports multiple Beam runners, each orchestrated through its respective Kubernetes Operator. These operators provide the necessary logic to manage the lifecycle of data processing jobs running on different engines, including:
Apache Flink Operator:
- Manages job submission, execution, scaling, and failure recovery for Flink-based data processing jobs.
Apache Spark Operator:
- Handles Spark jobs by submitting them to the Kubernetes cluster and manages their lifecycle (scheduling, scaling, resource management).
Samza Operator:
- Orchestrates the deployment and execution of Samza jobs in Kubernetes.
Each operator configures the required Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) that define how jobs and resources are represented within the Kubernetes cluster. These CRDs include specifications for job parameters, execution environment configurations, and resource allocation (e.g., CPU, memory).
Job submission and orchestration:
- Runners submit Beam pipelines as Kubernetes Jobs via custom CRDs.
Scaling and resource management:
- Dynamic scaling based on workload and predefined policies.
Failure handling and recovery:
- Automated failure detection and job recovery mechanisms.
Deployment:
The operators are deployed as part of the Beamstack installation. Helm charts or Kustomize templates are used to deploy the operators, ensuring ease of configuration across different clusters.
Worker Pool: Beamstack Harness
The Beamstack Harness is responsible for managing the pool of workers that execute the stages of Beam pipelines. These workers are dynamically provisioned within the Kubernetes cluster based on the resource requirements of the pipeline.
Key Responsibilities:
Worker Pod Management:
- Beamstack launches worker pods in the Kubernetes cluster based on the requirements of the submitted Beam pipeline.
Task Scheduling:
- Each worker processes a subset of tasks within a Beam pipeline. The Harness ensures task scheduling and load balancing across worker pods.
Resource Utilization Optimization:
- Beamstack ensures that worker resources (CPU, memory) are optimized for the workload, automatically adjusting the pool size based on job demand.
Monitoring Stack: Grafana, Prometheus
To ensure robust observability, Beamstack integrates with a monitoring stack that includes Prometheus for metrics collection and Grafana for visualization.
Prometheus:
Metrics collection:
- Prometheus scrapes metrics from Kubernetes components, the Beam Runners, and worker pods. This includes data such as job execution times, resource utilization (CPU, memory), pod health, and pipeline performance.
Grafana:
Visualization:
- Grafana provides dashboards that visualize real-time metrics and historical trends. Pre-built dashboards are included to track pipeline performance, resource utilization, and overall cluster health.
Custom Dashboards:
- Beamstack integrates custom Grafana dashboards to monitor specific aspects of their Beam pipelines or Kubernetes cluster.
Initialization and Configuration
When Beamstack is initialized on a target Kubernetes cluster, it sets up the necessary components to manage Beam pipelines. The initialization involves the following steps:
Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs)
The Beam Runners Operators configure their own CRDs within the cluster. These CRDs define the resources for job submission and execution.
Kubernetes Operators Deployment
Beamstack deploys Kubernetes Operators for Flink, Spark, Samza, etc. These operators are responsible for managing the jobs for each runner, ensuring that the correct resources are allocated, and that jobs are scheduled and monitored.
Monitoring Stack Setup
Beamstack installs Prometheus and Grafana into the cluster. Prometheus is configured to scrape metrics from the Beam Runners and worker pods, while Grafana is set up with pre-configured dashboards to visualize pipeline and cluster metrics.
Cluster Resource Configuration
Beamstack configures resource allocation strategies for running Beam pipelines efficiently. This includes setting up Horizontal Pod Autoscalers (HPAs), setting resource quotas, and configuring node selectors or taints/tolerations to ensure that workloads are assigned to the appropriate nodes.
Detailed Flow of Pipeline Execution
Pipeline Submission:
- A Beam pipeline YAML configuration is submitted via beamstack CLI
Job Submission:
- The Beam pipeline job is submitted via the chosen Beam Runner (e.g., Flink, Spark, Samza).
Job Scheduling:
- The Kubernetes Operator for the respective runner handles job scheduling, ensuring the required resources (worker pods) are available.
Worker Pool Execution:
- The Beamstack Harness manages the worker pods responsible for executing tasks within the pipeline. Tasks are distributed among the worker pods, and execution is monitored.
Metrics Collection:
- Prometheus scrapes real-time metrics from the worker pods and operators. These metrics are displayed in Grafana for monitoring.
Job Completion:
- Upon successful completion, the worker pods are terminated, and the results are stored or pushed to the configured data sinks.
Next steps
- Follow Installing Beamstack to set up your environment and install Beamstack.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it!.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.